The evil that men do lives after them; the good is oft interred with their bones.
William Shakespeare. Act 3, scene ii, Julius Caesar.
Bone in the body is a living tissue performing many functions in addition to providingmechanical support for the body. It is composed of a hard matrix of minerals (such as calcium and potassium salts) deposited around protein fibres (such as collagen).
In the developing foetus, the skeleton is first laid down as cartilage which is then replaced by bone. Bone X-rays, especially in young children, will still show areas of cartilage present at the ends of growing bones; this can be used to estimate a child’s age. However, even in adulthood, the size and shape of bones change, and are continuously being remodelled in response to everyday stresses. In fact, the entire human skeleton is replaced every 10 years, through the activities of bone-dissolving and bone-rebuilding cells.
Skeletal defects are common birth abnormalities and can be caused by a variety of different genes leading to more than 200 distinct diseases.
Decreased bone or cartilage growth usually leads to disproportionate short-stature – this differs to proportionate short stature for example seen in growth hormone deficiency. Depending upon which bones are primarily affected, such as in the limbs, trunk, or ribs, it is possible to differentiate by a glance some of the various types of disproportionate short-stature, and in some cases which gene might be involved, e.g. achondroplasia, pseudoachondroplasia, cartilage-hair hypoplasia, spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita, Ellis-van-Creveld syndrome, and primodial dwarfism).
Increased bone growth can lead to the bones becoming more brittle and in sever cases can lead to short disproportionate stature, deformed bone growth and increased fractures, e.g. osteopetrosis.
Deranged bone growth can in severe cases lead to massive deformity, e.g. Craniodiaphyseal dysplasia, Klippel-Feil syndrome, fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva and sclerosteosis.
Anchondroplasia
Autosomal dominant
1:25,000
Mutations in a gene reducing the ability of cartilage cells to develop into bone during development leads to achondroplasia (Gr. a; lack of, chondroplasia; cartilage growth). This results in reduced growth of the arms and legs though normal body trunk.
Jason ‘wee man’ Acuña the star of Jackass and a professional skateboarder has this condition.

A number of filmstars, such as actors Josh Ryan Evans and David Rappaport were also born with this.
From the discovery of numerous mummified bodies and skeletons it appears that achondroplasia was unusually common in ancient Egypt. This is possibly due to the fact that Egypt was a closed society for quite some time and there was a total acceptance of achondroplasia, allowing individuals with the condition to procreate without prejudice; in fact people with short stature may have been revered in ancient Egypt and the Egyptian gods, Bes and Ptah, are often depicted as having short stature.



Pseudoachondroplasia
Pseudoachondroplasia (Gr. pseudo; false) results from a the production of a toxic mutant protein in cartilage cells resulting in slow bone growth and dysproportional short stature.
Shimshon Eizik Ovitz passed on the mutation to seven of his ten children, who were subsequently were born with the condition and toured central Europe as entertainers known as the Lilliput Troupe, until sent to Auschwitz in May 1944. However, they were liberated by Russian troops, the family eventually found their way to a new home in Israel where they once again became successful performers.

Cartilage-hair Hypoplasia
Autosomal recessive
Rare
Cartilage-hair hypoplasia, is characterised by shortened arms and legs but normal body trunk (i.e. disproportionate short-stature) in addition to a low level of hair growth. This disease is autosomal recessively inherited from mutations in a gene important for cell division and growth.
Two of the most widely known people with this condition are the actors Billy Barty, who founded the organisation and charity Little People of America, and Verne Troyer, star of the Austin Powers films.


Spondyloepiphyseal Dysplasia Congenita
Spondyloepiphyseal dysplasia congenita is characterised by a shortened body trunk (individuals with achondroplasia have a normal sized trunk), in addition to the shortened arms and legs while the head, hands and feet are of normal size. This is a rare autosomal dominantly inherited disorder caused by defects in a gene coding for a collagen protein the main component of bone and cartilage.
The actor Warwick Davis, best known as Professor Flitwick in the “Harry Potter” movies, as the title character in “Willow”, as Wicket in “Star Wars”, has this


and the late American actor Michael Dunn, star of “The Wild Wild West” TV series was also affected by this condition.
Ellis-van-Creveld Syndrome
Ellis-van-Crevald results in shortened arms, legs and ribs and a small chest, in addition to the presence of more than the normal number of fingers or toes.


Though relatively rare (1 in 60,000), this recessive disorder, has a very high incidence (1 in 200) in the Old Order Amish of Pennsylvania. This is due to a founder effect as the Old Order Amish population stems from a small number of about 200 immigrants, including Samuel King and his wife who came to the area in 1744; one of these two must have carried a gene defect for the disorder.
Klippel-Feil Syndrome
Klippel–Feil syndrome are a heterogenous group of disorders characterized by the fusion of some of the vertebrae immdiately below the spine resulting in a short neck and restricted mobility of the upper spine. Different types of these diseases can autosomal dominant or recessively inherited through a number of different genes.It has been suggested that Pharaoh Tutankhamun suffered from Klippel–Feil syndrome, and the English cricketer Gladstone Small was also born with this disorder.

Craniodiaphyseal Dysplasia
Autosomal recessive
Rare
Craniotubular dysplasia (diaphysis; the hollow tube of cortical bone) result in abnormal bone shape due to excessive deposition of calcium causing new bone to form. Mild forms of these diseases, caused by accumulation of calcium in the synovial fluid around the joints, may only result in moderate knee problems while sever forms such as Craniodiaphyseal diaplasia resultin cranial thickening and the narrowing of cranial foramina (perforations in bones for nerves to pass through) resulting in blindness, deafness and facial palsy.
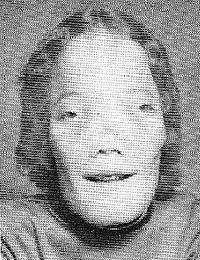
This disorder is depicted in the 1985 biographical movie called The Mask relating the life and early death of Roy L. “Rocky” Dennis, who suffered from this disease and died in 1980 at the age of 16.
Osteopetrosis
Osteopetrosis (Gr. osteo; bone, petros; stone) are a group of disorders characterised by increased production of bone or cartilage leading to them becoming very brittle. Mild types of this disorder such as Albers-Schönberg disease may result in weakened bones anddeafness resulting from mild bone overgrowth in the skull compressing nerves.
The American artist Laurel Burch suffered from this, suffering more than 100 bone fractures in her life as a result.
A more severe form is pycnodysostosis (Gr. pyknos; dense, dysostosis; abnormal bone formation) resulting in disproportionate short stature. Tolouse Lautrec inherited this disorder that a number of his cousins also shared. Standing was only 1.53 meters tall with short legs, he suffered numerous fractures associated with bone fragility.

Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva
Fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (fibro; fibrous connective tissue, ossification; process of bone formation, progressive) is a disorder where the body grows new bone at sites of the injury rather than the appropriate tissues.
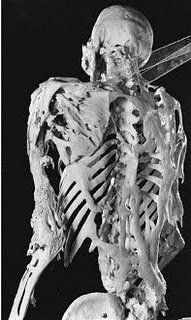
Occurring at a frequency of 1 in 2 million people the most well known sufferer was the American Harry Raymond Eastlack. At 10 years old he started developing painful nodules in the neck and shoulders which progressed until towards the end of his life he was able only to move his lips. Before he died of pneumonia he requested that his body be donated to science, and his skeleton is still on display at the Mutter Museum in Philadelphia showing how the muscles of his back had turned into sheets of bone.
Primordial Dwarfism
Primordial dwarfism is characterised by a body that is proportionately formed, but very small. There are a number of different syndromes displaying this phenotype such as Russell-Silver Syndrome, Seckel Syndrome, Meier-Gorlin Syndrome and types of Majewski Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism.
Lucia Zarate had Majewski Osteodysplastic Primordial Dwarfism Type II. Holding the Guinness World Record as the “lightest recorded adult”, weighing 2.1 kg at the age of 17. Exhibiting herself around the world she died of hypothermia in 1890 when her train became stranded in snow in the Sierra Nevada mountains.

Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (Gr. osteo, genesis; formation, imperfecta; imperfect), results from various mutations in collagen formation leading to brittle bones. Severe forms can present with short stature while mild forms can leave individuals with a normal appearance but weak bones.
The Viking Ivar Ragnarsson, who invaded and became King of England in 865 AD, suffered from one of the more severe types of this disease, acquiring the nickname Ivar the Boneless, as he was supposedly unable to walk on his legs and so had to be carried around on a shield.
Julie Fernandez the British actress, best known as Brenda, on the BBC comedy The Office also has a sever form of Osteogenesis Imperfecta.
Sclerosteosis
Undiagnosed milder forms of osteogenesis imperfecta have led to instances of child abuse allegations due to increased bone fractures and breaks. In one of many examples, a 4 month Liliana Valasquez in the US was taken away from her parents after the hospital discovered multiple rib fractures. Not until 18 months was Liliana diagnosed with the disease and returned to her parents who have since had another child with the disorder.

Autosomal recessive
Rare
Sclerosteosis and van Buchem disease result from increased activity of osteoblasts (cells responsible for bone formation) leading to progressive bone and skeletal overgrowth, especially in the skull. Sufferers generally appear normal at birth though develop enlargement of the lower jaw, deafness and facial paralysis in childhood and can be life-threatening complications if the overgrowing skull compresses parts of the part of the brain. Van Buchem disease is generally milder than sclerosteosis.
Sclerosteosis and van Buchem disease result from mutations in the SOST gene that provides instructions for making the protein sclerostin whose role is to inhibit bone formation.
It has been suggested that the tenth-century Viking, Egill Skallagrímsson, might have suffered from this disease as pictures of him show a very prominent jaw and skull deformity.